Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
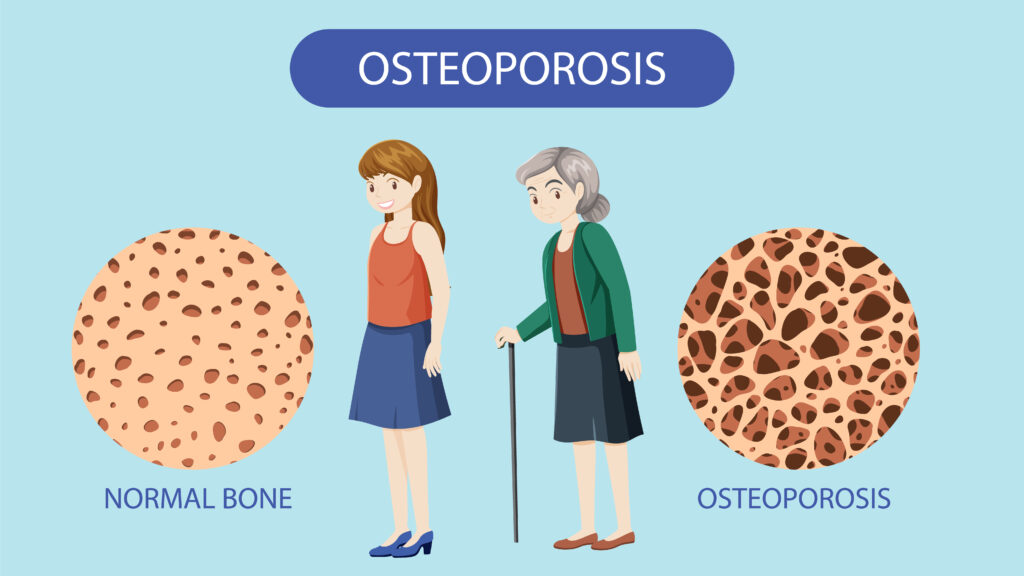
Osteoporosis is a condition in which bones become porous, weak, and brittle. Due to low bone density, even a small fall or minor pressure can cause fractures.
Osteoporosis risk increases in the following groups:
In the early stages, osteoporosis has almost no noticeable symptoms. However, some warning signs may include:
Bones are constantly breaking down and rebuilding. In osteoporosis, bones break down faster than they rebuild.
Major causes include:
Osteoporosis can be prevented by adopting healthy daily habits:
Milk, curd, cheese, leafy greens, almonds
15–20 minutes of morning sunlight or supplements (if required)
Weight-bearing exercises such as walking, yoga, and light weight training
A DEXA Scan is recommended after age 50 to check bone density
If diagnosed with osteoporosis, your doctor may recommend:
This content is for general awareness and informational purposes only. It is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always consult a qualified healthcare provider for personalized medical guidance.